The Easiest Way to Green Your Fleet

When we speak to our fleet customers about priorities, one topic frequently rises to the top: sustainability. Whether it’s because of internal/corporate social responsibility commitments or regulations, fleet managers are under pressure to “green” their fleets.
While use of biofuels is one viable pathway, they are mostly constrained to diesel-engine vehicles. Which leaves electric vehicles as the new shiny object. There are many benefits to EVs, including sustainability, lower total cost of ownership and the brand halo that comes from investing in EVs.
But for those who manage very large, complex fleets, swapping out many or most internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles for EVs is likely to be cost-prohibitive.
Turns out there’s a solution available to every fleet owner today that allows them to reduce their emissions while keeping their existing vehicles. Better yet, the solution also helps them save money.
The Cost of Idling
The average vehicle emits about a pound of CO2 every 10 minutes while idling. That may not seem like much, but if you have 100 vehicles and each idles 30 minutes a day, that’s 200 lbs of CO2 produced. Over the course of a year, that’s more than 50,000 pounds, or 25 tons, of CO2.
If you wanted to reduce emissions by that same amount, you’d have to remove about two mid-size fleet vehicles that average 25,000 miles per year from your fleet.
Idling also wastes fuel. According to AAA, the average vehicle burns about ¼ gallon per gas every 15 minutes. Using the same metrics as above (and assuming gas at $3.50/gal), this means your drivers waste about $45,000 year.
Last, but not least, idling is illegal in several states, including Massachusetts, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Vermont, Hawaii, parts of California, Colorado, New York, Ohio, Utah and others. Non-compliance can result in hefty fees.
So it’s in your best financial interests to reduce idling.
Chances are this is not a new idea or concept for you. What is new, however, are tools that make it easy for fleet managers to track and report on idling. As the saying goes, you can’t improve what you can’t measure.
Thanks to today’s on-board telematics connected to Motorq’s secure, cloud-based data analytics platform, Wheels is able to track the prevalence and impact of idling vehicles (and their drivers) across the fleet. Dashboard reports make it easy for fleet managers to clearly see the idling behavior of every vehicle and driver.
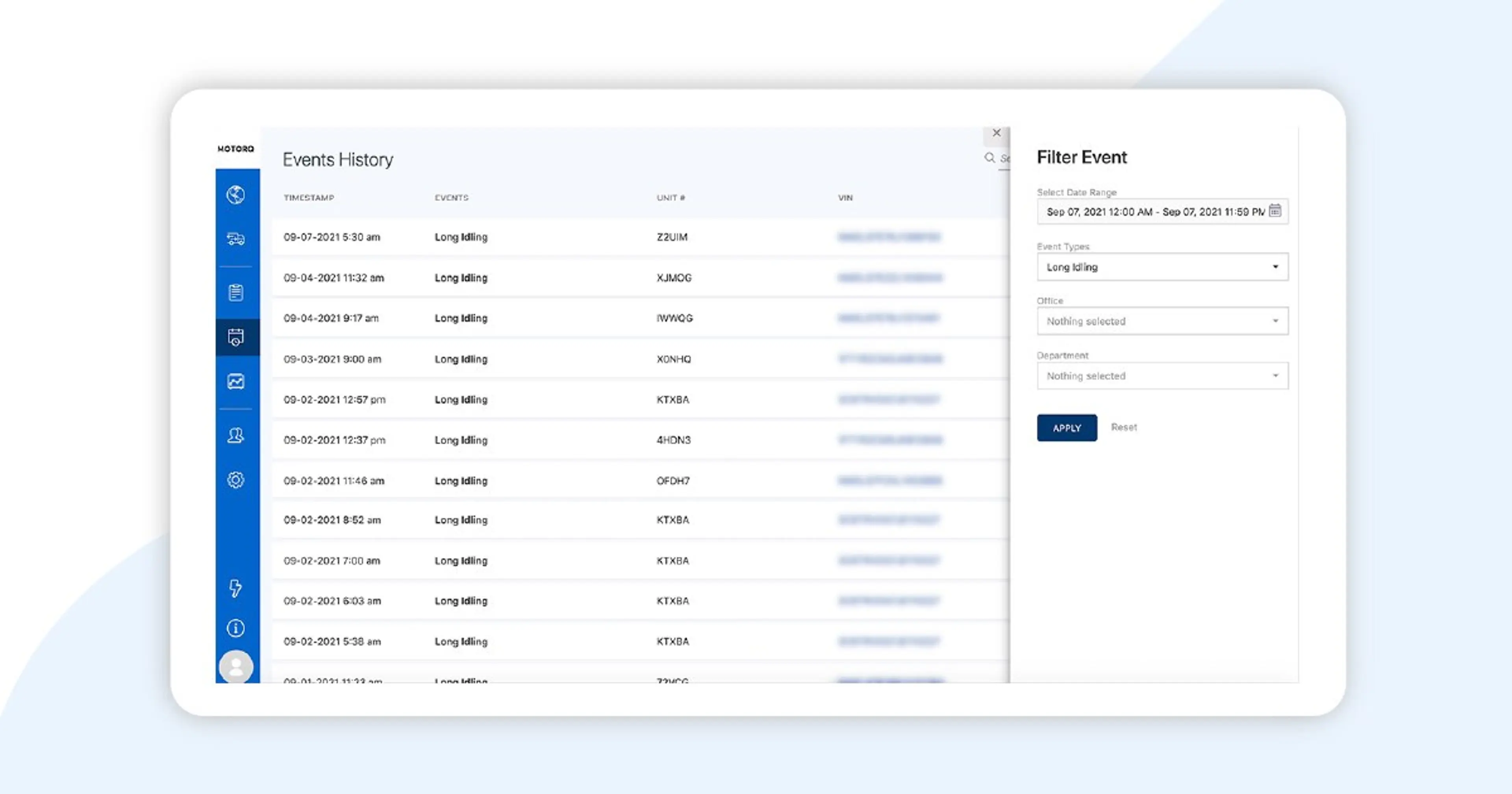
How to Measure Idling
Want to know total minutes of idling per day? By driver? By VIN? Total “excessive” idling events? How about “all of the above.”
It’s all possible, and it’s all happening for Wheels fleet customers today. Motorq’s platform injests and analyzes multiple data feeds from the vehicle, across multiple telematics partners, and creates a customized report for fleet managers. Regarding idling, the report details the number of minutes of idling for each VIN in the fleet.
From there, it’s easy to see if excessive idling is an issue for any particular drivers, branches, regions, day of the week, months of the year, or any other attribute you’d like to track this against, as well as if it’s a problem in the aggregate, even if there are no/few instances of excessive idlers.
How to Improve Idling
With actual data, fleet managers can set in place a course of action designed to reduce idling. Examples include 1-1 meetings with drivers to go through the data and set a plan in place for improvement. For fleet-wide issue, the aggregate report can be used for goal setting and incentives; it can even be added to a driver scorecard. This could also be used to get various divisions to compete to see who can reduce idle time the most.
So, before you invest in new hybrids or full EVs (or even if you do) to meet your sustainability goals, consider adopting connected car data analytics. You can not only reduce idling, but also improve many other facets of your fleet.
The article was co-authored by Arun Rajagopalan, co-founder and CEO of Motorq, and Shannon Keck, Product Manager at Wheels.